Clotrimazole: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: topical solution
Drug classes: Topical antifungals, Vaginal anti-infectives
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Oct 29, 2024.
On This Page
FOR EXTERNAL USE ONLY.
NOT FOR OPHTHALMIC USE.
This product is also available without a prescription.
Rx only
Clotrimazole Description
Clotrimazole Topical Solution USP, 1% contains 10 mg clotrimazole USP, a synthetic antifungal agent having the chemical name 1-(o-Chloro-α,α-diphenylbenzyl) imidazole with the following structural formula:
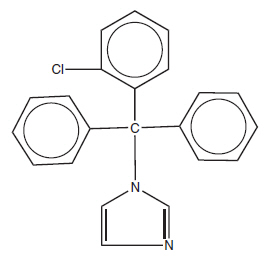 | |
| Molecular Formula C 22H 17ClN 2 | Molecular Weight 344.85 |
Clotrimazole is an odorless, white crystalline substance. It is practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in ether and very soluble in polyethylene glycol 400, ethanol, and chloroform.
Each mL of Clotrimazole Topical Solution, USP 1% contains 10 mg clotrimazole USP in a nonaqueous vehicle of polyethylene glycol 400.
Clotrimazole - Clinical Pharmacology
Clotrimazole is a broad-spectrum antifungal agent that is used for the treatment of dermal infections caused by various species of pathogenic dermatophytes, yeasts, and Malassezia furfur. The primary action of clotrimazole is against dividing and growing organisms.
In vitro, clotrimazole exhibits fungistatic and fungicidal activity against isolates of Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Epidermophyton floccosum, Microsporum canis,and Candida species including Candida albicans. In general, the in vitroactivity of clotrimazole corresponds to that of tolnaftate and griseofulvin against the mycelia of dermatophytes ( Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton),and to that of the polyenes (amphotericin B and nystatin) against budding fungi ( Candida). Using an in vivo(mouse) and an in vitro(mouse kidney homogenate) testing system, clotrimazole and miconazole were equally effective in preventing the growth of the pseudomycelia and mycelia of Candida albicans.
Strains of fungi having a natural resistance to clotrimazole are rare. Only a single isolate of Candida guilliermondihas been reported to have primary resistance to clotrimazole.
No single-step or multiple-step resistance to clotrimazole has developed during successive passages of Candida albicans and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. No appreciable change in sensitivity was detected after successive passages of isolates of C. albicans, C. krusei, or C. pseudotropicalisin liquid or solid media containing clotrimazole. Also, resistance could not be developed in chemically induced mutant strains of polyene-resistant isolates of C. albicans.
Slight, reversible resistance was noted in three isolates of C. albicanstested by one investigator. There is a single report that records the clinical emergence of a C. albicansstrain with considerable resistance to flucytosine and miconazole, and with cross-resistance to clotrimazole; the strain remained sensitive to nystatin and amphotericin B.
In studies of the mechanism of action, the minimum fungicidal concentration of clotrimazole caused leakage of intracellular phosphorus compounds into the ambient medium with concomitant breakdown of cellular nucleic acids and accelerated potassium efflux. Both these events began rapidly and extensively after addition of the drug.
Clotrimazole appears to be well absorbed in humans following oral administration and is eliminated mainly as inactive metabolites. Following topical and vaginal administration, however, clotrimazole appears to be minimally absorbed.
Six hours after the application of radioactive clotrimazole 1% cream and 1% solution onto intact and acutely inflamed skin, the concentration of clotrimazole varied from 100 mcg/cm 3, in the stratum corneum to 0.5 mcg/cm 3to 1 mcg/cm 3in the stratum reticulare, and 0.1 mcg/cm 3in the subcutis.
No measurable amount of radioactivity (≤ 0.001 mcg/mL) was found in the serum within 48 hours after application under occlusive dressing of 0.5 mL of the solution or 0.8 g of the cream.
Only 0.5% or less of the applied radioactivity was excreted in the urine.
Following intravaginal administration of 100 mg 14C-clotrimazole vaginal tablets to nine adult females, an average peak serum level, corresponding to only 0.03 mcg equivalents/mL of clotrimazole, was reached 1 to 2 days after application. After intravaginal administration of 5 g of 1% 14C-clotrimazole vaginal cream containing 50 mg active drug, to five subjects (one with candidal colpitis), serum levels corresponding to approximately 0.01 mcg equivalents/mL were reached between 8 and 24 hours after application.
Indications and Usage for Clotrimazole
Prescription Clotrimazole Topical Solution product is indicated for the topical treatment of candidiasis due to Candida albicansand tinea versicolor due to Malassezia furfur.
This formulation is also available as a nonprescription product which is indicated for the topical treatment of the following dermal infections: tinea pedis, tinea cruris, and tinea corporis due to Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Epidermophyton fluoccosum, and Microsporum canis.
Contraindications
Topical antifungal agents are contraindicated in those patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of the components of the preparation.
Precautions
General
If irritation or sensitivity develops with the use of clotrimazole, treatment should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted.
Information for Patient
This information is intended to aid in the safe and effective use of this medication. It is not a disclosure of all possible adverse or intended effects.
The patient should be advised to:
- Use the medication for the full treatment time even though the symptoms may have improved. Notify the physician if there is no improvement after 4 weeks of treatment.
- Inform the physician if the area of application shows signs of increased irritation (redness, itching, burning, blistering, swelling, oozing) indicative of possible sensitization.
- Avoid sources of infection or reinfection.
Laboratory Tests
If there is lack of response to clotrimazole, appropriate microbiological studies should be repeated to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other pathogens before instituting another course of antimycotic therapy.
Drug Interactions
Synergism or antagonism between clotrimazole and nystatin, or amphotericin B, or flucytosine against strains of C. albicanshas not been reported.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
An 18-month oral dosing study with clotrimazole in rats has not revealed any carcinogenic effect.
In tests for mutagenesis, chromosomes of the spermatophores of Chinese hamsters which had been exposed to clotrimazole were examined for structural changes during the metaphase.
Prior to testing, the hamsters had received five oral clotrimazole doses of 100 mg/kg body weight. The results of this study showed that clotrimazole had no mutagenic effect.
Usage in Pregnancy
The disposition of 14C-clotrimazole has been studied in humans and animals. Clotrimazole is very poorly absorbed following dermal application or intravaginal administration to humans. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY)
In clinical trials, use of vaginally applied clotrimazole in pregnant women in their second and third trimesters has not been associated with ill effects.
There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Studies in pregnant rats with intravaginal doses up to 100 mg/kg have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to clotrimazole.
High oraldoses of clotrimazole in rats and mice ranging from 50 mg/kg to 120 mg/kg resulted in embryotoxicity (possibly secondary to maternal toxicity), impairment of mating, decreased litter size and number of viable young and decreased pup survival to weaning. However, clotrimazole was notteratogenic in mice, rabbits and rats at oral doses up to 200 mg/kg, 180 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg, respectively. Oral absorption in the rat amounts to approximately 90% of the administered dose.
Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used only if clearly indicated during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions have been reported in connection with the use of clotrimazole: erythema, stinging, blistering, peeling, edema, pruritius, urticaria, burning, and general irritation of the skin.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Akron Pharma, Inc. at 1-877-225-6999 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Overdosage
Acute overdosage with topical application of clotrimazole is unlikely and would not be expected to lead to a life-threatening situation.
Clotrimazole Dosage and Administration
Gently massage sufficient Clotrimazole Topical Solution, USP 1% into the affected and surrounding skin areas twice a day, in the morning and evening.
Clinical improvement, with relief of pruritus, usually occurs within the first week of treatment with Clotrimazole Topical Solution, USP 1%. If the patient shows no clinical improvement after 4 weeks of treatment with Clotrimazole Topical Solution, USP 1% the diagnosis should be reviewed.
How is Clotrimazole supplied
Clotrimazole Topical Solution, USP 1% is supplied as follows:
NDC 71399-0666-3 in 30 mL round bottle in carton
NDC 71399-0666-6 in 2 x 30 mL round bottles in a carton
| CLOTRIMAZOLE TOPICAL SOLUTION USP, 1%
clotrimazole topical solution usp, 1% solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Akron Pharma Inc. (067878881) |
Frequently asked questions
More about clotrimazole topical
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (32)
- Drug images
- Latest FDA alerts (2)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: topical antifungals
- Breastfeeding



